Gegeben sind 4 Punkte A, B, C, D in einem kartesischen Koordinatensystem:
A( 2 | 2 | -2 )
B( 4 | -4 | 2 )
C( 8 | 2 | 2 )
D( 6 | 8 | -2 )
Aufgabe I
Zeige, dass das Dreieck ABC gleichschenklig ist!
Lösung:
Wir prüfen ob zwei Seiten des Dreiecks dieselbe Länge haben:


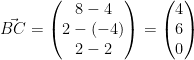

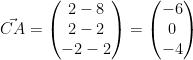

und
haben die gleiche Länge, also ist das Dreieck ABC gleichschenklig.
Aufgabe II
Prüfe, ob 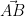 und
und 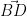 zueinander orthogonal sind!
zueinander orthogonal sind!
Lösung:
Falls die beiden Vektoren orthogonal sind, müsste ihr Skalarprodukt Null sein:
und
sind nicht orthogonal.
Aufgabe III
Die Diagonale 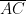 des Vierecks ABCD schneidet die x-y-Ebene im Punkt S(xS|yS|zS). Berechne die Koordinaten von S!
des Vierecks ABCD schneidet die x-y-Ebene im Punkt S(xS|yS|zS). Berechne die Koordinaten von S!
Lösung:
Die Diagonale 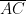 liegt auf der Geraden
liegt auf der Geraden


Der Punkt S liegt in der x-y-Ebene, also ist zS = 0 und S liegt auf der Geraden .
| xS | = | 2 + r · 6 |
| yS | = | 2 + r · 0 |
| 0 | = | -2 + r · 4 |
Die unterste Zeile liefert r = 1/2 , die mittlere Zeile yS = 2 und die oberste durch Einsetzen von 1/2 in r noch xS = 5.
Es ist S( 5 | 2 | 0 ).